Conclusion of the Union Budget 2022
In her Union Budget Speech for 2022-23, FM Nirmala Sitharaman asked for ‘sab ka prayaas’ to bring ‘amrit kaal’ to the economy by laying forth a roadmap to aid the country transit onwards and upwards from India at 75 years. In a nutshell, Omega Financial decodes the budget for you.
The points with the most emphasis are discussed here.
A large capital expenditure budget, conservative tax aims, no relief for the salaried middle class, and a new crypto tax are all on the table.
Apart from that here is the Fine Print of the Budget with all the figures:
- RBI led Digital Rupee using blockchain to be launched in FY23, By the end of March 2023, Sitharaman announced, the Reserve Bank of India would introduce the digital currency or “digital rupee.”
- No change in income tax slab: Most individuals were dissatisfied because there were no modifications to the income tax slabs, which they had hoped for.
- PLI (Production Linked Incentive scheme) in 14 sectors for Aatmanirbhar Bharat to create 6 million jobs, an additional allocation of Rs 19,500 crore for PLI in solar PV module manufacturing.
- Rs 48,000 crore allocated to housing projects under PM Housing Scheme for FY23.
- ₹ 19,500 crores will be spent to improve the solar capacity that has already been built.
- GDP growth for FY 22 is expected to be 2%, the highest for any large economy.
- 8 million new dwellings in rural, urban areas to be completed under PM Awas Yojana.
- Rs 2.37 trillion worth of MSP direct payments to wheat and paddy farmers.
- Rs 2 trillion outlay for MSMEs, Additional loans for 13 Million MSMEs.
- New provision to file the updated return within 2 years of the relevant assessment year.
- The alternate minimum tax for cooperative societies is down from 18.5% to 15%.
- Tax exemption to start-ups extended to March 2023.
- The corporate tax surcharge has been reduced from 12 percent to 7%.
- Duty on unpolished diamonds to be reduced to 5%.

- ₹ 39,44,909 Crores totals the Government spending: “The Budget of 2022 is highly balanced and follows the gradual growth-oriented approach of the previous budget,” remarked Ashishkumar Chauhan, MD & CEO, BSE. In 2022-23, the government plans to spend Rs 39,44,909 crore, while total receipts (excluding borrowings) are expected to be Rs 22,83,713 crore.
- ₹ 7,50,246 crores in capital expenditures: “With a CAPEX target of 7.50 lakh crore and incentives and announcements across multiple different industries, the government is seeking to restore growth in the economy,” said Vaibhav Agrawal, CIO and founder of Teji Mandi. Banking, infrastructure, and manufacturing exports are anticipated to benefit.”
- Disinvestment Receipts totalling ₹ 65,000 crores: For the fiscal year 2023, the government expects disinvestment receipts of Rs 65,000 crore. Although last year’s Disinvestment aim was not met, the government is sure that it would meet this year’s target by divesting companies such as Life Insurance Company Pvt. Ltd and others.
- 4% of GDP — Fiscal Deficit in Fiscal Year (FY) 23: “The revised fiscal deficit is marginally larger than the budgeted print,” Suman Chowdhury, the chief analytical officer at Acuité Ratings & Research, said. Because of the large increase in capital spending in FY23, the fiscal deficit is only expected to shrink by 6.4 per cent next year.
- Income from digital assets such as cryptocurrency and NFTs is subject to a 30% tax.
- The PMAY scheme has been allocated a total of ₹ 48000 crores.
- PM Gati-shakti masterplan Has scope to enhance Multimodal communication through 7 engines, 2000 km of the rail network to be brought under KAVACH & Highway network to grow by 25,000 km in FY23. “As expected, infrastructure development is a focus area of Union Budget 2022,” stated Acuité Ratings & Research’s Suman Chowdhury. The infrastructure activities have generally been bundled under the “PM Gati Shakti Master Plan.” The emphasis on the speedier movement of goods and people will undoubtedly help to alleviate supply limitations and boost export competitiveness. The investment in freight ports, logistics parks, railway modernization, and, most critically, transportation system integration is noteworthy.”
- 15% maximum surcharge on Long Term Capital Gains: Long-term capital gains on publicly traded stock/shares or units are subject to a maximum surcharge of 15%, while other long-term capital gains are subject to a graded surcharge of up to 37%.
- 75 Digital Banking Units in 75 Districts: “75 Digital Banking Units across 75 Districts by Scheduled Commercial Banks is a great step,” stated Nilaya Varma, co-founder and CEO of Primus Partners. These small efforts must prepare the way for the launch of new banking models that are 100 percent digital, offer better services, reduced lending costs, and higher depositor returns.”
- Customs duty on steel scrap extended by a year.
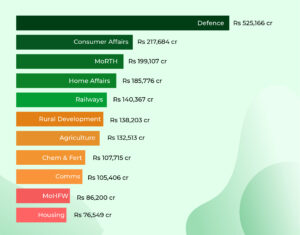
- 68% of the capital outlay will be for the domestic defence industry. Defence gets the highest allocation this time, clearly marking the priorities of the government.